Terpene Education
Terpene Education is at the forefront of everything we do.
We believe that cannabis terpenes are highly important to the overall experience. To help you discover your preferred terpenes, we created our color-coded terpene bouquet. The terpene bouquet represents a product's terpene profile by using the colors that we’ve assigned for each terpene.
As you try different products, we hope this tool will help you identify the terpenes that suit your preferences and help you quickly spot them on our menu.
Check out our list below for information on the color, associated botanicals, and interesting facts about each terpene.
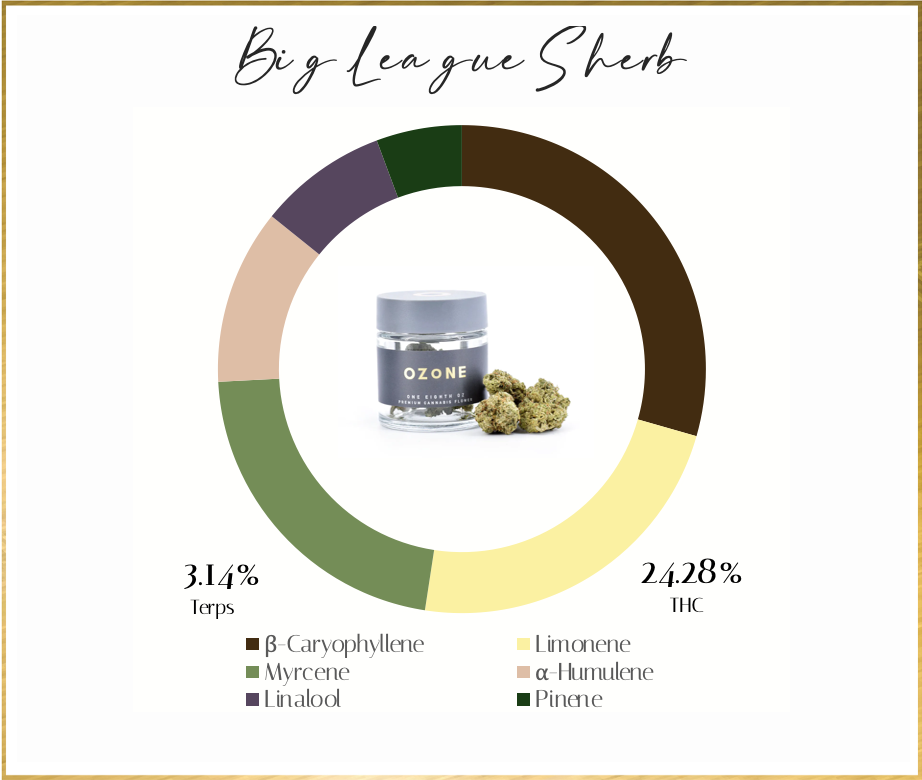
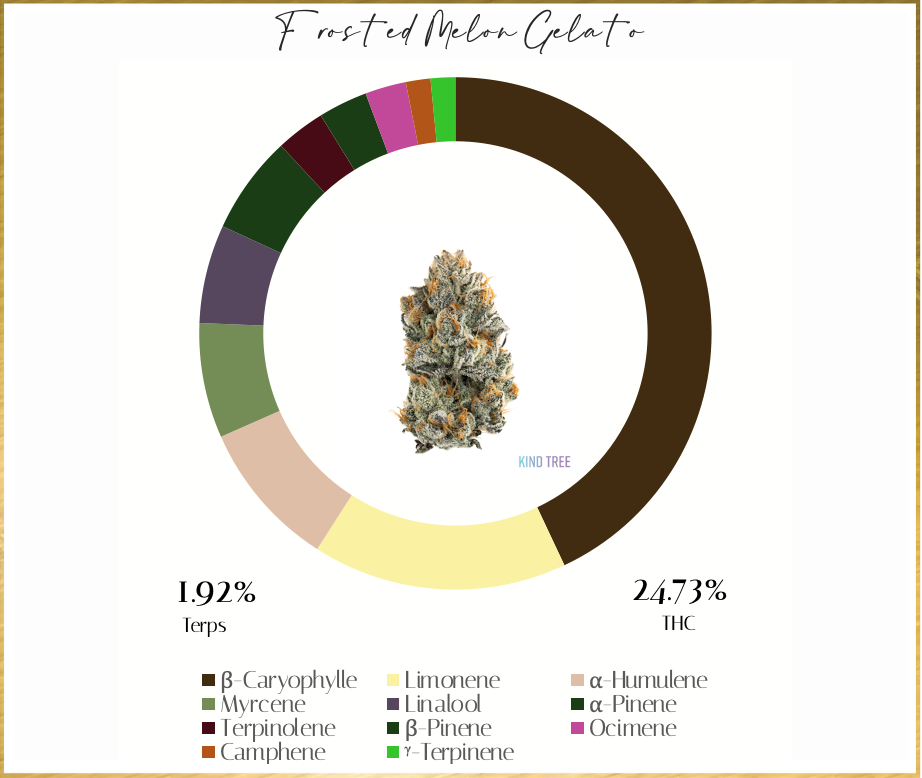
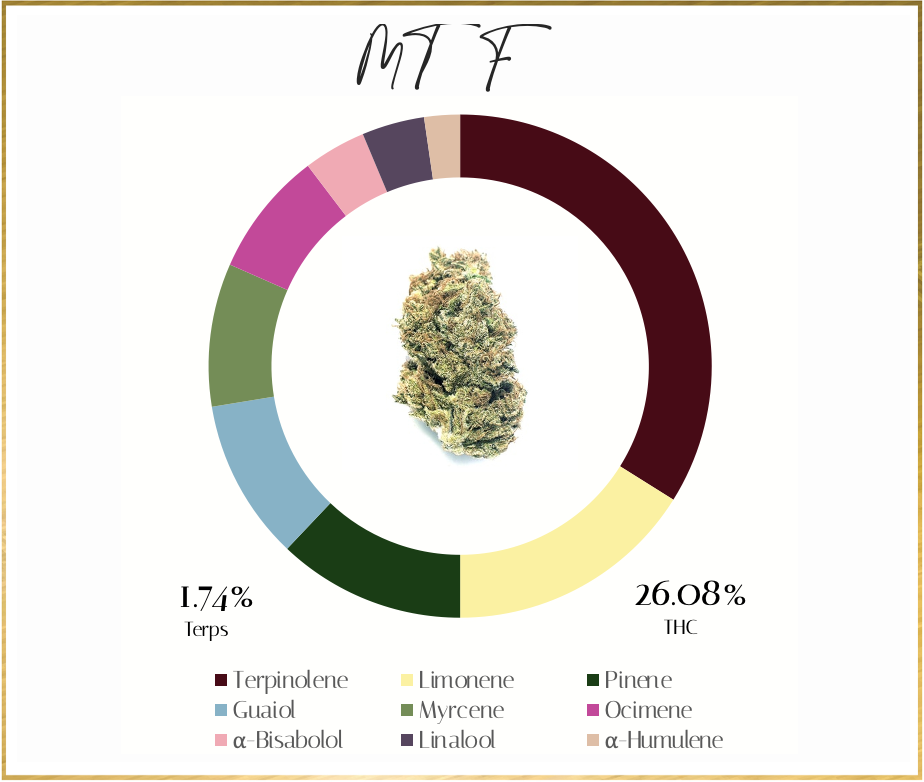

Common Questions
-
◉ Terpenes - the essential oils that determine the scent of many flowers, herbs and fruits - give cannabis its distinctive aroma and flavor.
◉ Cannabis can exhibit over 150 different terpenes. Like THC and CBD, these naturally-occurring compounds are found in the trichomes of female cannabis plants.
◉ Several factors such as genetics, growing conditions, harvesting, drying, curing, and packaging can all influence terpene levels of the product you eventually purchase.
◉ Although most cannabis terpenes are present in only trace amounts, the mix of minor terpenes and dominant terpenes give each cannabis strain their diverse signature scent profiles.
◉ Many terpenes are volatile compounds, meaning over time they’ll dissipate. This will happen in normal conditions, and more quickly in suboptimal conditions.
-
◉ We are still learning about terpenes and their interactions with cannabinoids. Indeed, the majority of current research is based on animal models.
◉ In addition to their purpose for scents and flavoring, humans have long harnessed terpenes from botanicals to formulate essential oils for practices such as aromatherapy.
◉ Terpenes have also been identified as a new frontier in cannabis medicine, alongside cannabinoids such as THC and CBD.[1]
◉ Some of the effects terpenes have on humans are evocative of their function in cannabis and other plants—like helping to fight off unwelcome microbes and pathogens.
◉ Emerging evidence suggests that plant compounds in cannabis, such as cannabinoids and terpenes, work together synergistically. This is known as the entourage effect. For example, some research has shown terpenes appear to play a part in influencing the effects of cannabinoids in the body. [2]
◉ More recent research has found that terpenes boost cannabinoid activity (but high concentrations of terpenes were needed to see this enhancement)
-
◉ Cannabis is often labeled as "sativa," "indica," or "hybrid" and meant to suggest different effects on the mind and body (for example, a sativa would be uplifting, while an indica would be calming)
◉ However, recent research has debunked this notion, revealing that the sativa/indica classification is largely misleading and lacks scientific basis. [1]
◉ Prior studies have uncovered significant discrepancies between advertised sativa/indica labels and the actual genetic makeup of the products, concluding that there is little consistency among strains sold under the same name, rendering the sativa/indica labeling unreliable and misleading. [1][2]
◉ To better serve our customers, we are moving away from this outdated system and towards cannabis terpenes, which we believe to be a more reliable and better choice factor and will help customers make more informed decisions.
Sources:
https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/terpenes-the-flavors-of-cannabis-aromatherapy
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01200
https://thecannabisscientist.com/testing-processing/high-and-too-dry
https://sn.astm.org/?q=features/two-cannabis-standards-you-should-know-about-.html
Dominant Terpenes
Terpenes List
Botanicals: cloves, basil, cinnamon, black pepper, oregano
Facts: One of cannabis’ most common terpenes
Shown to bind directly to endocannabinoid receptors
Botanicals: lemons, orange peel, citrus
Facts: Several therapeutic benefits have been studied, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gastroprotective effects, among others
Ongoing research regarding limonene’s potential anti-stress effects
Botanicals: Pine, conifers, sage, ironwort
Facts: One of the most prevalent terpenes in nature
High amounts of pinene may provide the mental health benefits experienced during “forest bathing”
Might reduce short-term memory impairment associated with THC
Botanicals: Thyme, hops, lemon grass, mango, cardamom
Facts: May have sedative and stress reducing properties
May lowering resistance across the blood brain barrier, leading to an increase in transportation of cannabinoids
Minor Terpenes
Terpenes List
Botanicals: Guava, chamomile
Facts: One of the “most-used herbal constituents” in the world
Has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and smooth muscle relaxant properties
Botanicals: Beautyberries
Facts: Traditionally used in Chinese medicine as a “messenger drug” - facilitating the effects of other drugs
Shown to have certain neuroprotective effects
Botanicals: Conifers, nutmeg, ginger
Facts: With a woody and earthy aroma, it is commonly used in the fragrance industry
In an ointment with menthol and other essential oils, camphene reduced experimentally induced bronchospasm in animals, suggesting application in humans
Botanicals: Camphor tree berries and bark
Facts: A common ingredient in some topical and vaporized medications intended to treat musculoskeletal pain or symptoms of common flu-like illnesses
Found in some old formulations of mothballs
Botanicals: Turpentine oil, cedar, rosemary
Facts: Various therapeutic properties including anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal, and sedative effects
Botanicals: Cedar, juniper, cypress
Facts: Cedarwood oil - in which cedar is a main constituent - has been shown to exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, antifungal activity, analgesic activity, antimicrobial activity, astringent properties, antibacterial activity, and neuroprotective activity
Botanicals: Cedar, juniper, cypress
Facts: Cedrol is a natural crystalline sesquiterpene alcohol found in the essential oil of conifers especially cedar wood
Has been shown to exhibit antioxidant and anticancer properties
Botanicals: Cumin, thyme, marjoram
Facts: Research suggests that cymene can combat inflammation and be an effective analgesic in a 2012 mouse study. Cymene, via thyme essential oil, was also shown to have antimicrobial properties in this 2014 study.
Botanicals: Eucalyptus, chrysanthemums
Facts: Commonly used in the management of syndromes like asthma, airway mucus hypertension, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
In one study, had a measurable impact on the cognitive and behavioral status of elderly persons who were cognitively impaired
Botanicals: Green apples, olive oil, hops, gardenia
Facts: Found in many complex essential oils with carminative (gas reduction) properties
Botanicals: Grapes, basil, daisies
Facts: One study looked into fenchol’s efficacy as an antibacterial against more than 60 strains of bacteria and found that, while it was not as effective as penicillin, it did inhibit bacterial growth.
Botanicals: Absinthe (wormwood), fennel
Facts: Has exhibited antimotility properties
Botanicals: Roses, geraniums
Facts: One of the most common molecules in the flavor and fragrance industries
Known to exhibit insecticidal and repellent properties and used as a natural pest control agent exhibiting low toxicity
Botanicals: Guaiacum trees, cypress trees
Facts: Studies in 2010 showed guaiol has anti-inflammatory properties in vitro (in a test tube) and in vivo (in a living organism)
Guaiacum trees have been used in natural medicine for some time. By the late 1700s, guaiacum gum extracted from the wood was being used in the treatment of syphilis and to regulate menstruation.
Botanicals: Ginseng, hops, sage
Facts: Has exhibited anti-inflammatory properties
Present in many therapeutic-grade essential oils and the use of such oils for healing purposes dates back centuries. The terpene is present in Balsam fir oil and is believed to be an active mechanism in fighting tumors.
Isoborneal
Botanicals: Geraniums, citronella
Facts: Studies indicate that geranyl boasts a number of therapeutic properties, such as antimicrobial action.
Has been used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat diverse complaints including digestive problems and swelling.
Botanicals: Spearmint, peppermint, lemon grass
Facts: Widely used for its flavoring and anesthetic properties
Botanicals: Chlorophyll, soybeans, green teas
Facts: Known for its grassy aroma and is often used as a precursor in the manufacturing of synthetic vitamins E and K1, and as a food additive
Botanicals: Frankincense, ginger, eucalyptus
Facts: Produces a minty, woody, and mildly citrus aromatic profile
A staple in holistic Eastern medicine for a long time, used for its antifungal and antibacterial properties
Botanicals: Lavender, jasmine, cinnamon, citrus
Facts: Commonly found as major component of essential oils of several aromatic species, many of which are used traditionally as sedatives
Mice exposed to linalool vapors show reduced levels of anxiety and lower depression-like behaviors.
Botanicals: Snapdragons, kumquats, basil, bergamot
Facts: In the perfume industry, ocimene is commonly used for its sweet, floral, and herbaceous aromatic profile.
In a 2013 study, essential oil with ocimene was shown to have anti-oxidative properties and the ability to inhibit key enzymes connected to type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Botanicals: “Lady of the Night” Orchids, roses, neroli
Facts: Used in traditional Persian medicine as an antiseizure and anticonvulsant natural agent.
Botanicals: Frankincense, ginger, eucalyptus
Facts: Produces a minty, woody, and mildly citrus aromatic profile
A staple in holistic Eastern medicine for a long time, used for its antifungal and antibacterial properties
Botanicals: Chlorophyll, soybeans, green teas
Facts: Known for its grassy aroma and is often used as a precursor in the manufacturing of synthetic vitamins E and K1, and as a food additive
Botanicals: Nutmeg, black pepper
Facts: Sabinene has shown promise for anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits
Botanicals: Lavender, jasmine, cinnamon, citrus
Facts: Commonly found as major component of essential oils of several aromatic species, many of which are used traditionally as sedatives
Mice exposed to linalool vapors show reduced levels of anxiety and lower depression-like behaviors.
Botanicals: Snapdragons, kumquats, basil, bergamot
Facts: In the perfume industry, ocimene is commonly used for its sweet, floral, and herbaceous aromatic profile.
In a 2013 study, essential oil with ocimene was shown to have anti-oxidative properties and the ability to inhibit key enzymes connected to type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Botanicals: “Lady of the Night” Orchids, roses, neroli
Facts: Used in traditional Persian medicine as an antiseizure and anticonvulsant natural agent.
Botanicals: Frankincense, ginger, eucalyptus
Facts: Produces a minty, woody, and mildly citrus aromatic profile
A staple in holistic Eastern medicine for a long time, used for its antifungal and antibacterial properties
Botanicals: Asiatic pennywort, tea tree, bergamot
Facts: The primary chemical constituent of tea tree oil
Botanicals: Pine cones, pine sap
Facts: Often said to have a “fresh” scent.
At least one study showed terpinolene acted as a sedative in mice, though subjective reports in humans suggest greater stimulation in terpinolene-rich strains
Botanicals: Lilac
Facts: Frequently used to create pleasant aromatic profiles in products like soap, lotion, and perfume, and it contributes to the distinctive, pine smoke-based aroma of lapsang souchong tea
Terpineol is most frequently found in strains also containing high levels of pinene
Botanicals: Grapefruit, oranges
Facts: Said to produce euphoric, uplifting feelings
Also been found to have anti-inflammatory properties, and is noted to be a powerful insecticide for repelling ticks and mosquitos

VISIT US
Visit Our Shop By Appointment
Whether you’re an experienced consumer or looking for your first experience, we’re looking forward to helping you.
Blue Violets’ mission is to become one of New Jersey’s finest cannabis dispensaries through our focus on exceptional product quality, unique consumer education, and positive community impact.
































